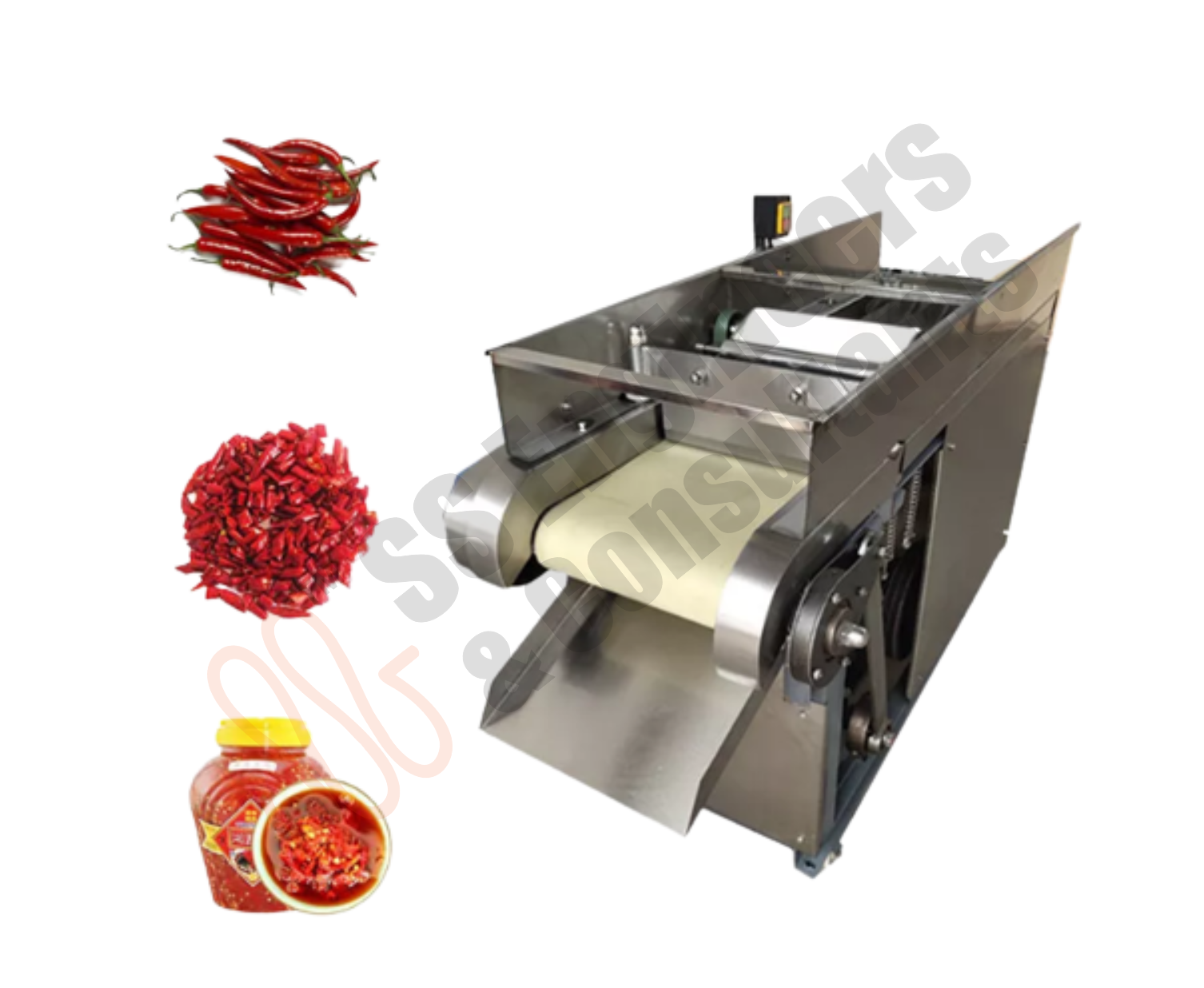
Categories
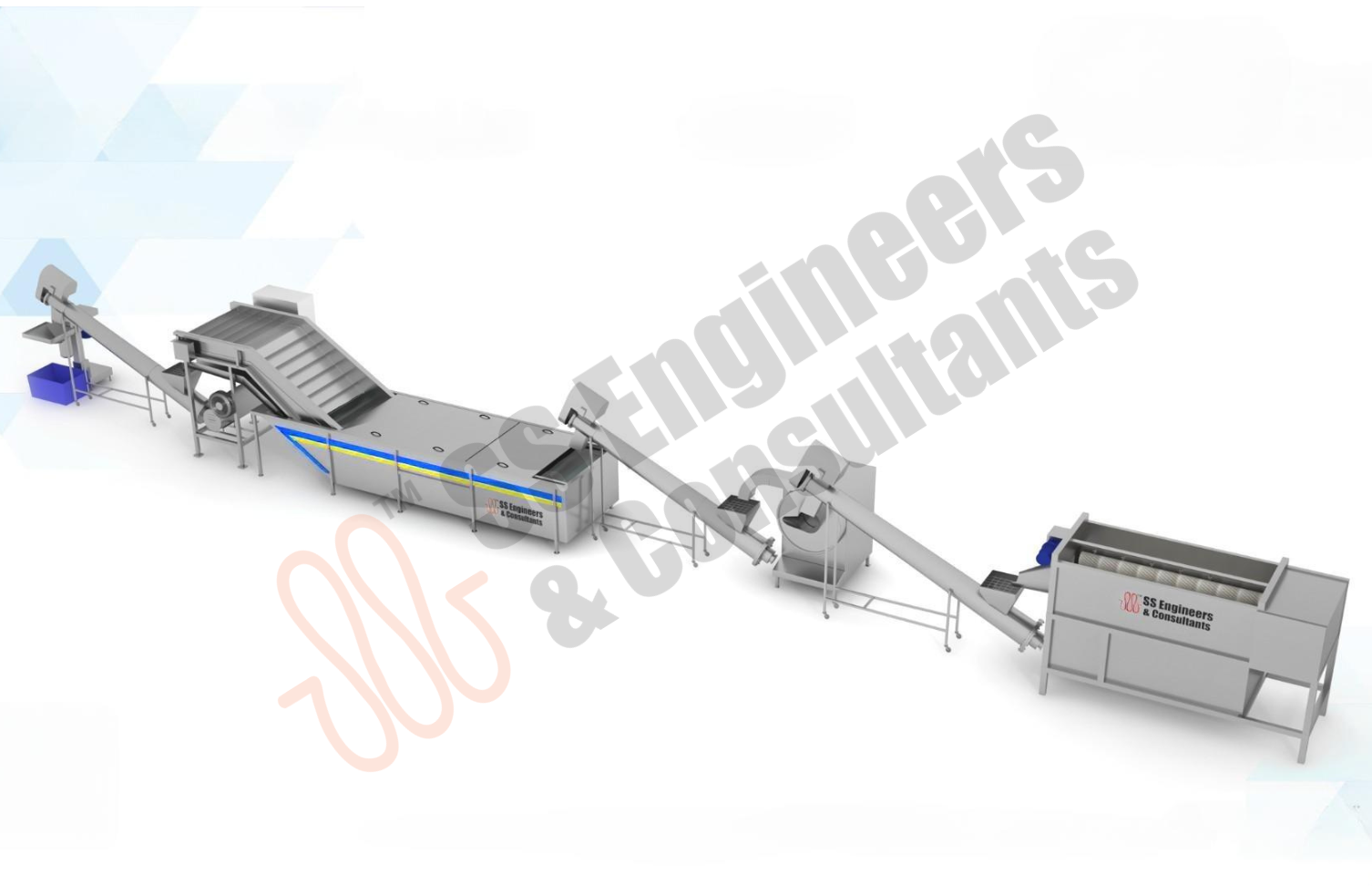
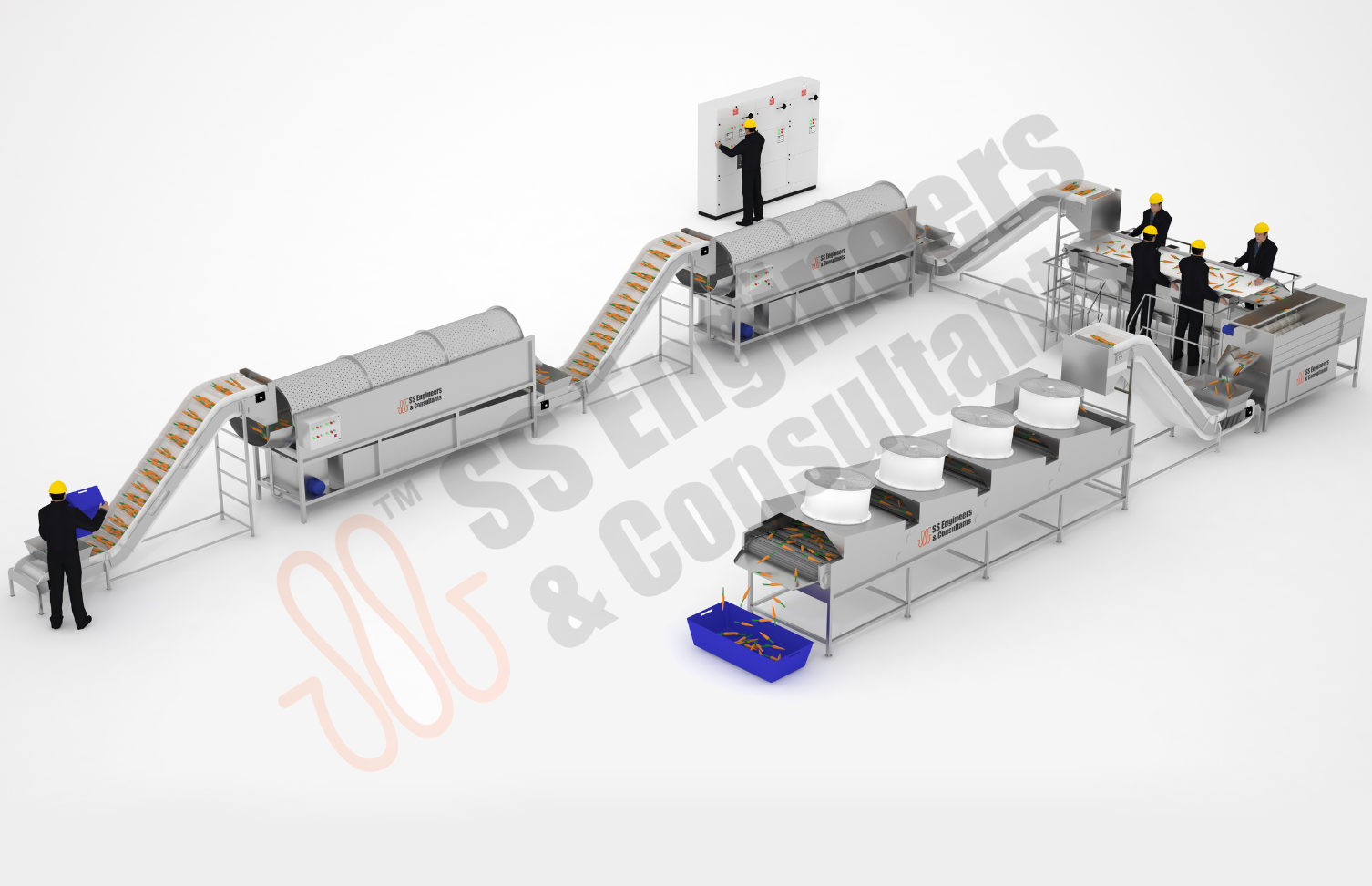
Root Vegetables Washing ,Sorting & Granding Line
Elevate your fruit and vegetable processing with SS Engineers & Consultants, India’s trusted manufacturer of high-performance machinery. Equip your facility with our advanced washing machines, air dryers, juice extractors, juice filling machines, and Fruit Juice Sterilization Machines, all crafted for efficiency and durability.
Choose our reliable and innovative Automatic Juice Filling Machine to boost productivity and ensure consistent quality. Every machine is designed to enhance output and support businesses in meeting industry standards with ease and reliability.
- Heavy-duty stainless-steel and food-grade construction ensuring hygiene and durability
- Automated root vegetable washing, brushing, and drying system for thorough cleaning of mud and soil
- Integrated sorting and grading system for accurate size, weight, and quality classification
- Adjustable water flow and brushing intensity to handle different types of root vegetables (potato, carrot, beet, radish, etc.)
- Modular design adaptable for small, medium, and large-scale pack house operations
- Compatible with conveyor belts, peeling systems, and packaging lines
- Energy- and water-efficient technology to reduce operational costs and improve sustainability
See it in Action
Need Custom Solutions?
Our team can develop specialized cleaning solutions tailored to your specific automotive cleaning requirements.
Contact Our Experts