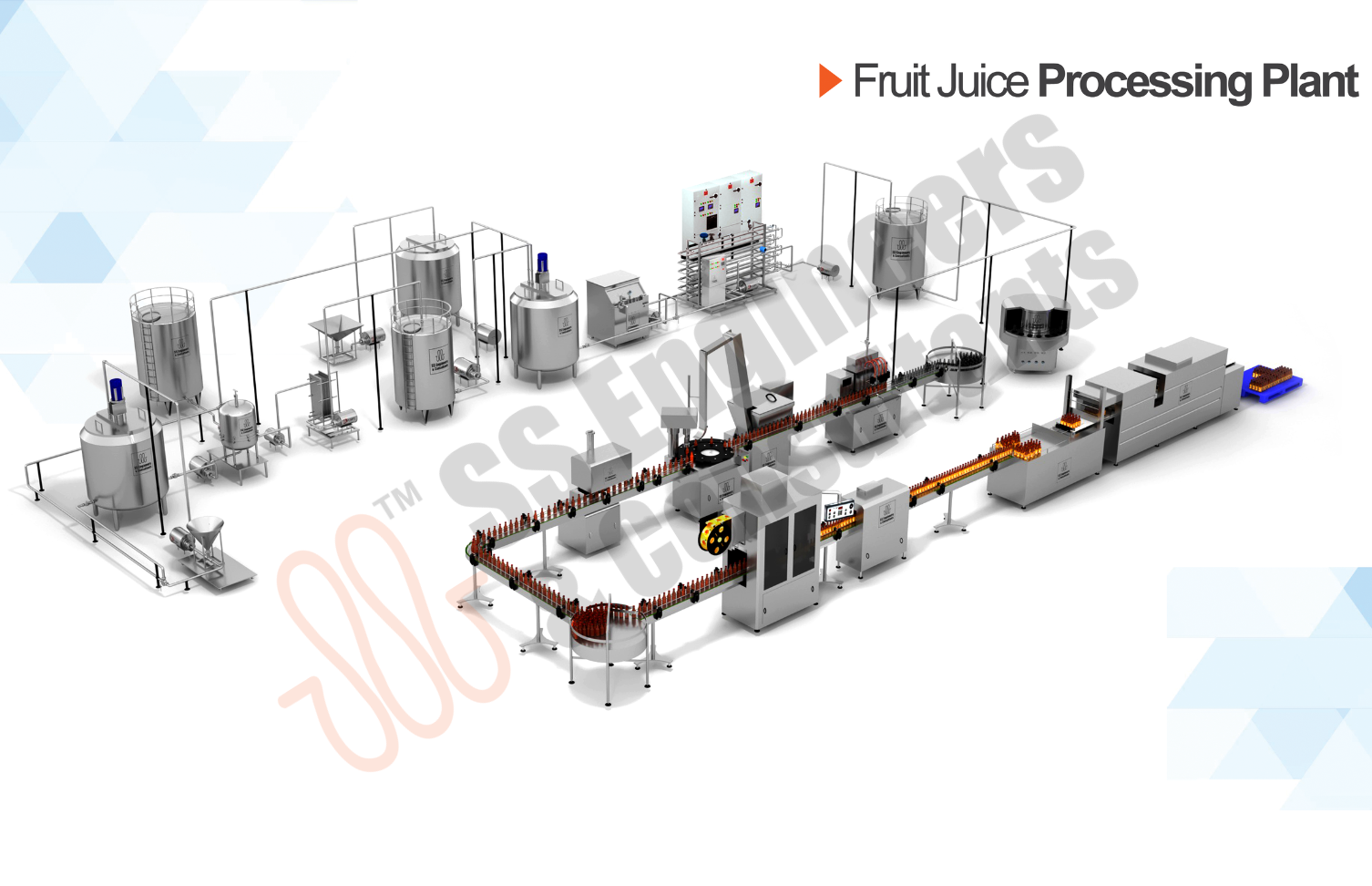
Categories
Powder-Processing-Plant
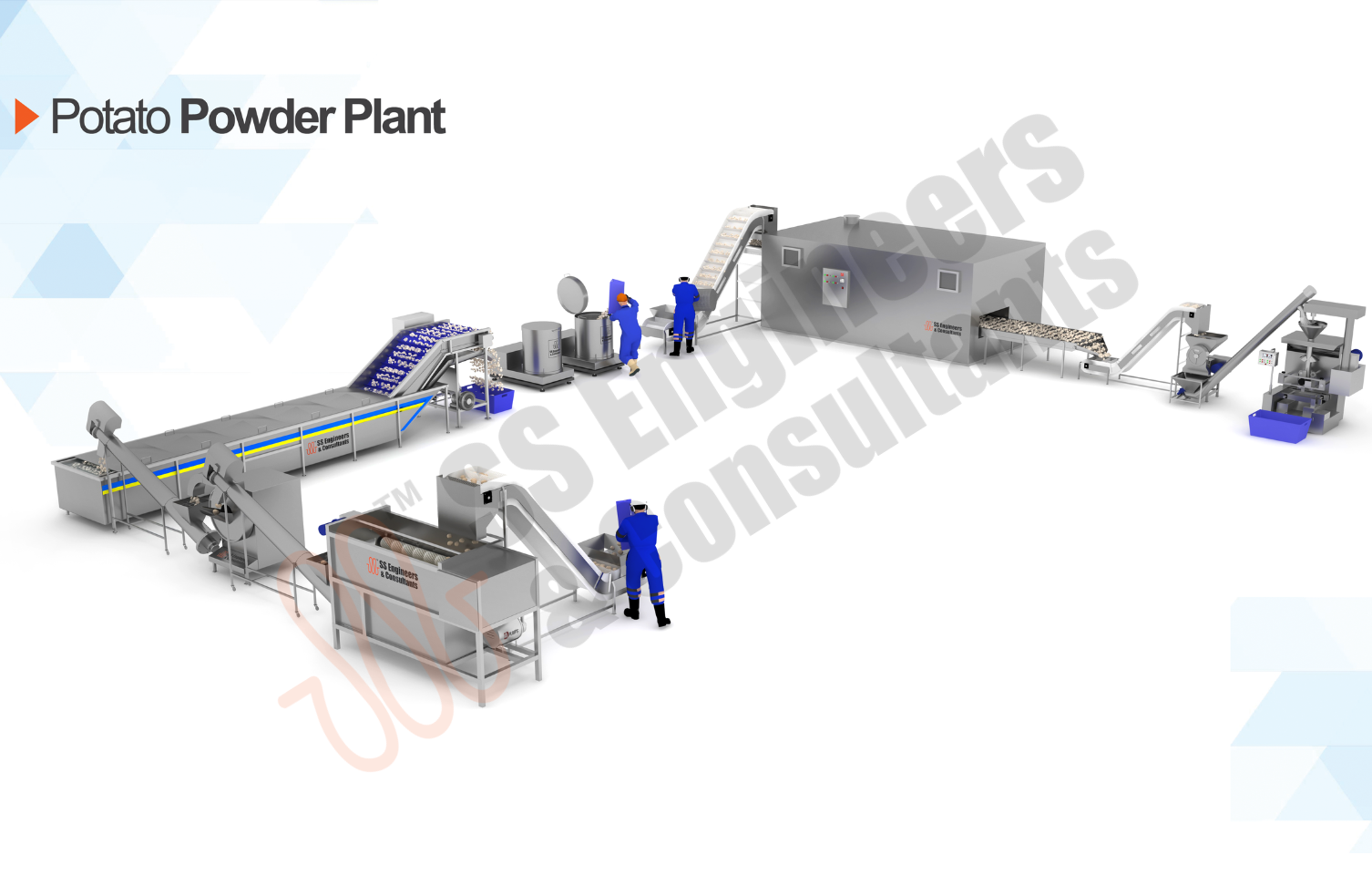
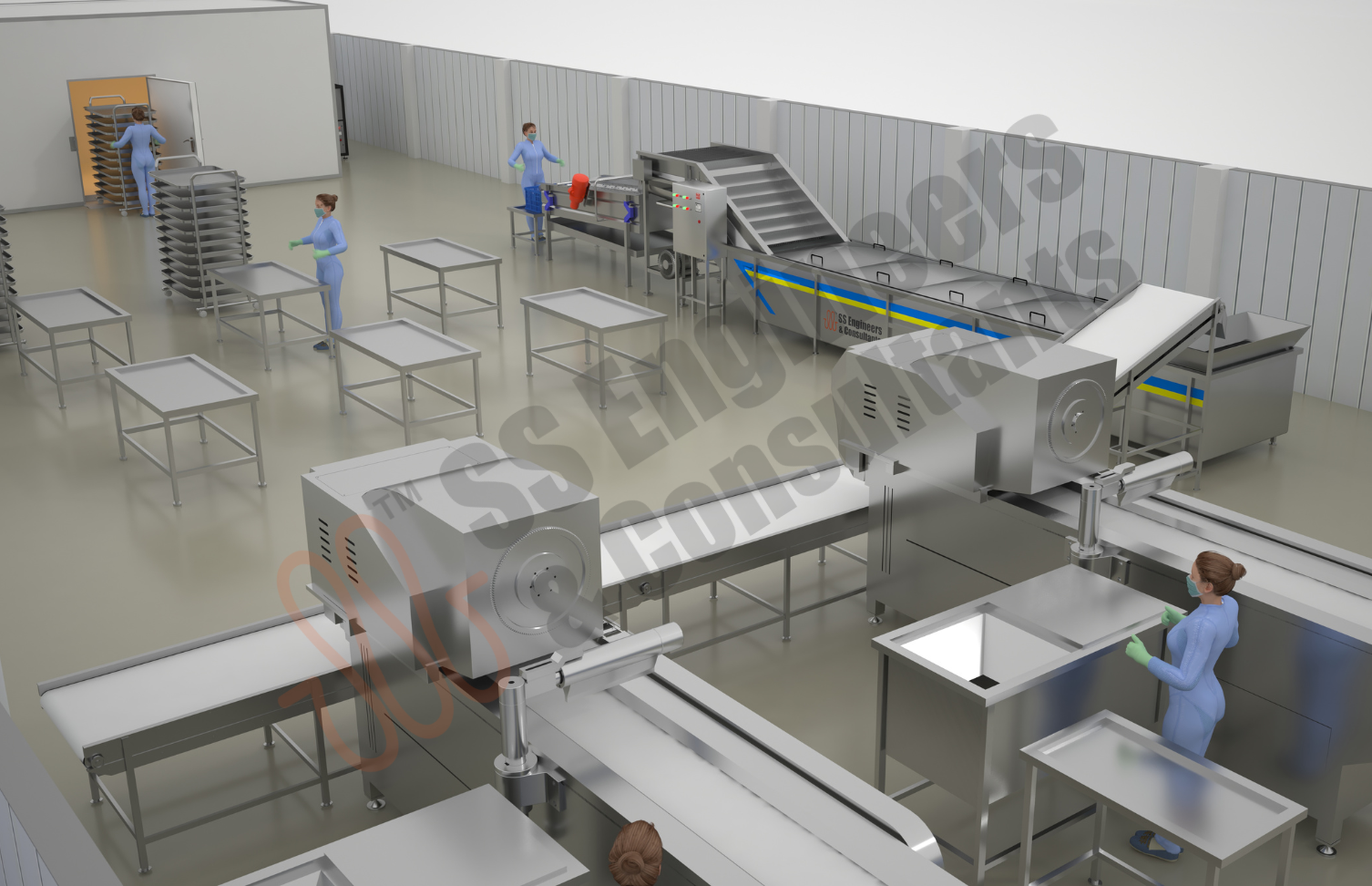
Streamline your production with SS Engineers & Consultants' complete line of equipment for Powder Processing Plants, designed for precise and efficient powder manufacturing. Our advanced solutions ensure optimized operations and high-quality output across a variety of powder products.
Leverage our industry expertise to enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Each piece of equipment is engineered for reliability, making our powder processing solutions a powerful asset for your facility's success.
- Robust stainless-steel construction ensuring hygiene and long-lasting durability
- Automated grinding, milling, and sieving system for uniform powder quality
- Integrated CIP (Clean-in-Place) system for quick and hygienic cleaning
- Precise temperature and moisture control to preserve product quality and shelf life
- Modular design adaptable for various food powders, spices, and herbal products
- Compatible with dairy, fruit, vegetable, and grain-based powders for versatile applications
- Energy-efficient drying and processing technology to minimize operating costs