Categories
Fruit Juice Plant
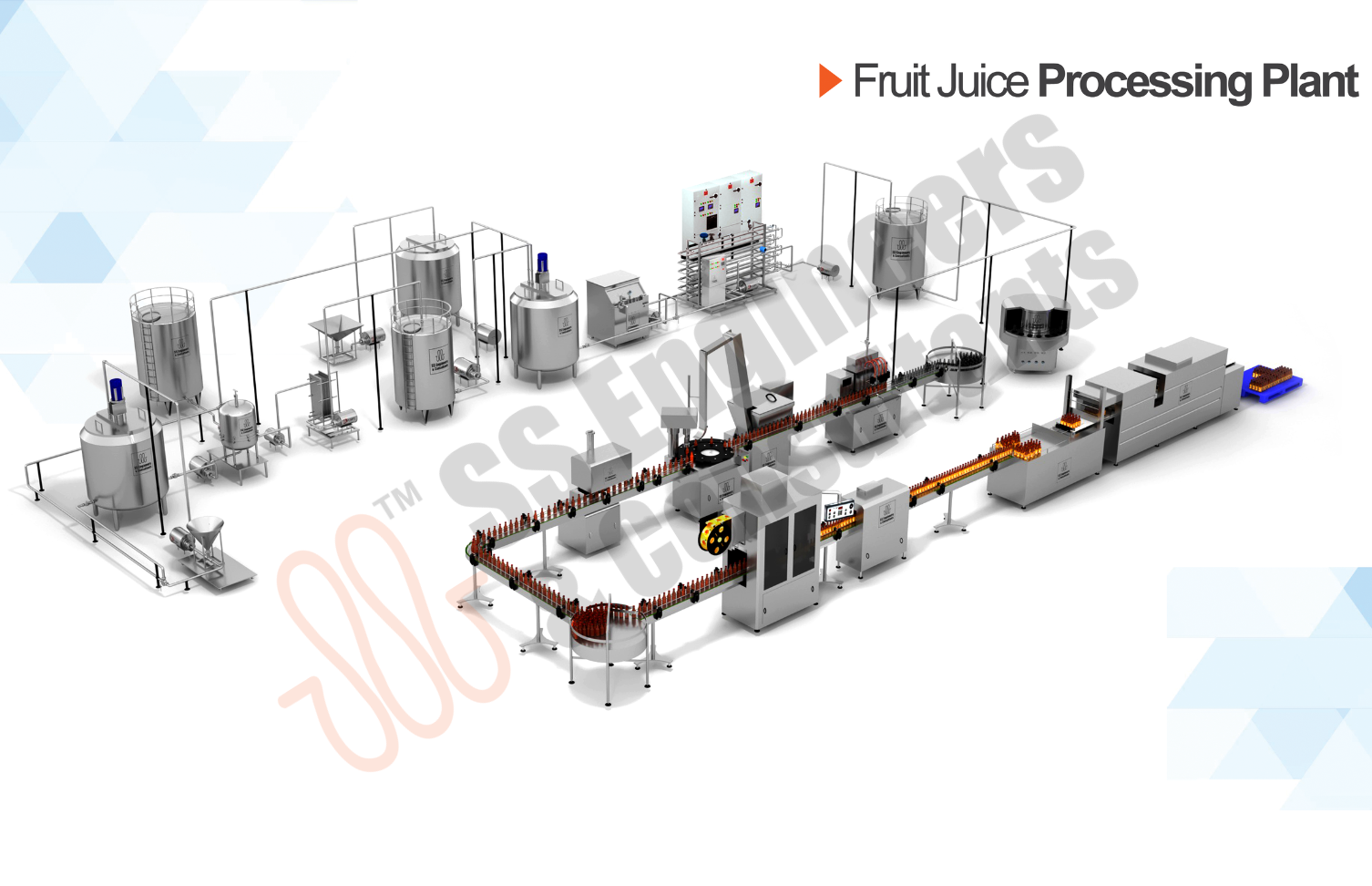
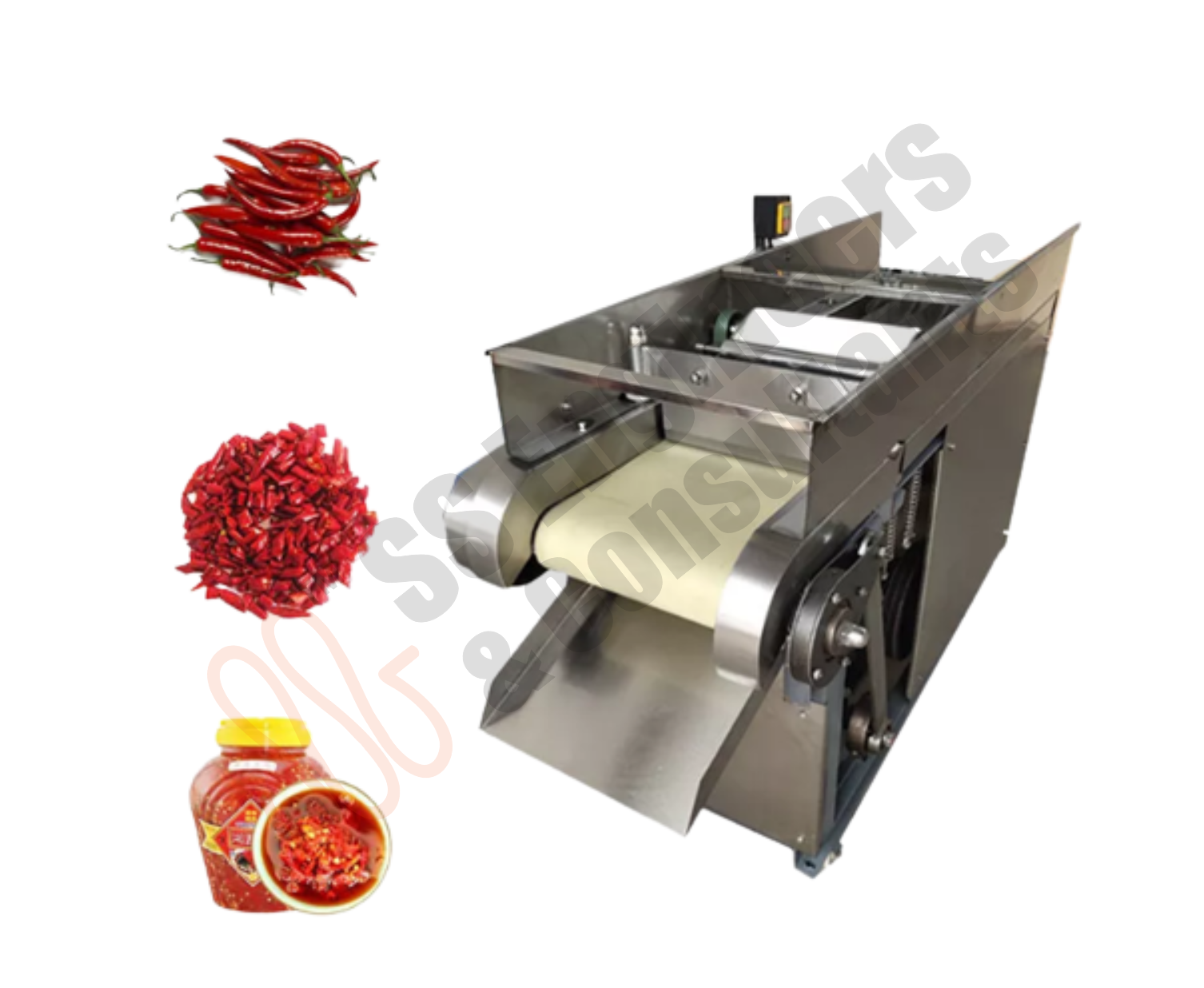
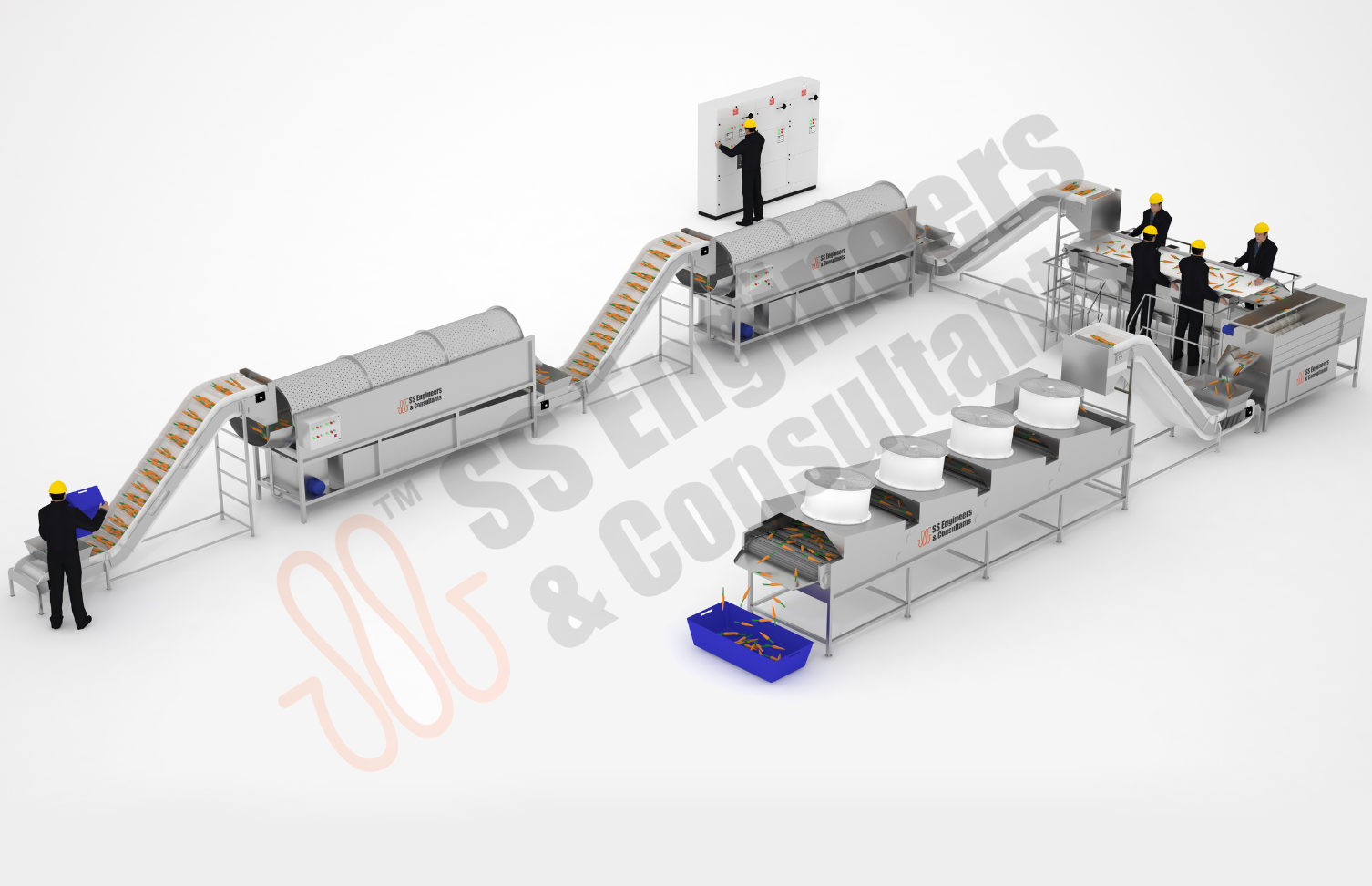
Enhance your production line with SS Engineers & Consultants, a leading manufacturer of fruit and vegetable processing machinery in India. Our advanced equipment—including washing machines, air drying machines, juice extractors, and juice filling machines—ensures efficient processing and high-quality output for your produce.
Rely on our expertise for durable and innovative solutions like the Automatic Juice Filling Machine and Fruit Juice Sterilization Machine, built to streamline operations and meet industry standards. Each machine is engineered for reliability and designed to boost productivity, making it an ideal choice for modern processing facilities.
- Robust stainless-steel construction ensuring hygiene and long-lasting durability
- Automated fruit washing, crushing, and juice extraction system for consistent product quality
- Integrated CIP (Clean-in-Place) system for efficient and hygienic cleaning
- Precise temperature and pasteurization control to preserve nutrients and flavor
- Modular design adaptable for mango, citrus, pomegranate, and other fruit juices
- Compatible with aseptic filling, bottling, and pouch packaging systems
- Energy-efficient processing technology to reduce operational costs and improve productivity
See it in Action
Need Custom Solutions?
Our team can develop specialized cleaning solutions tailored to your specific automotive cleaning requirements.
Contact Our Experts