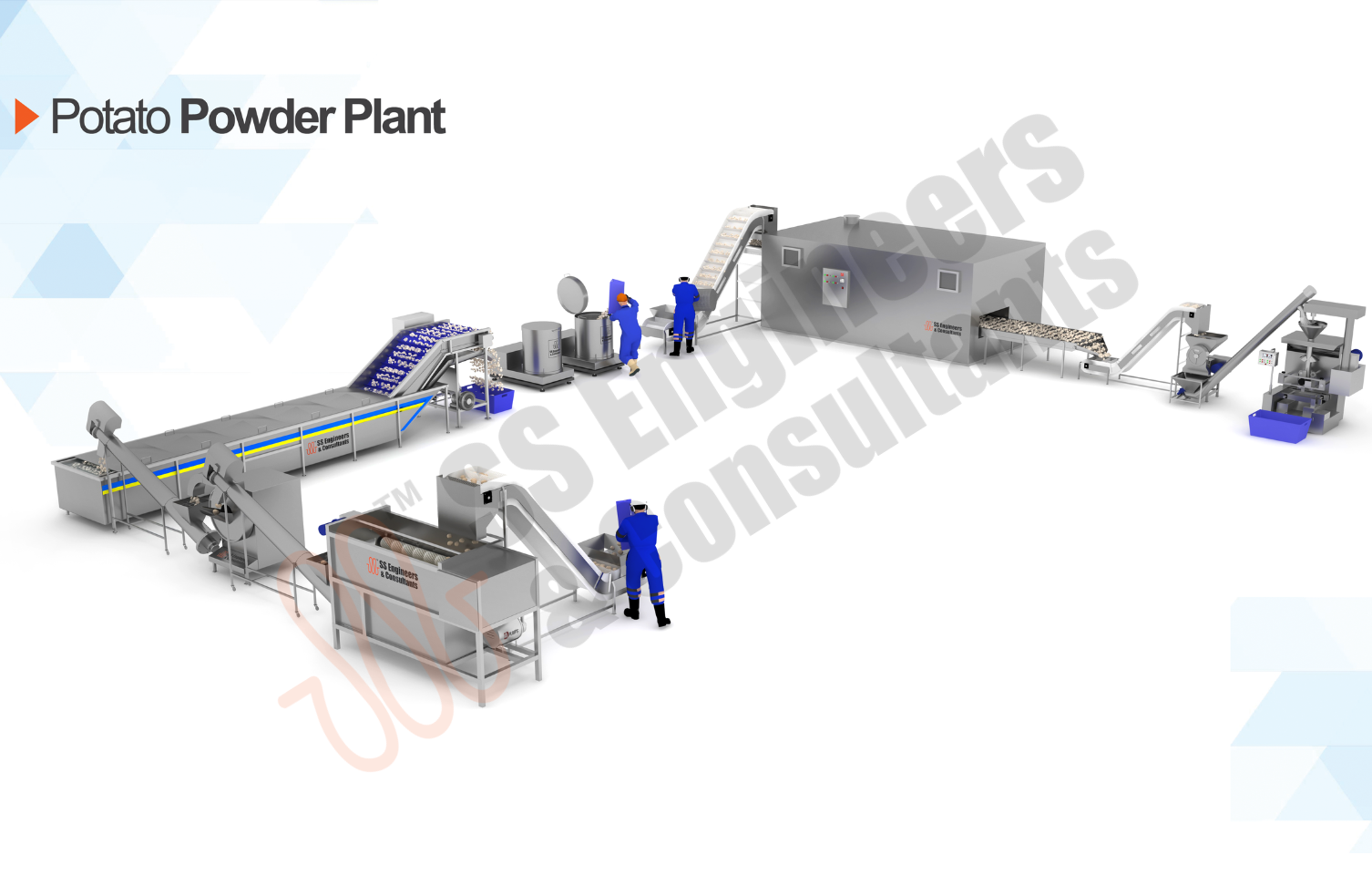
Categories
Fruits & Vegetable Pack House
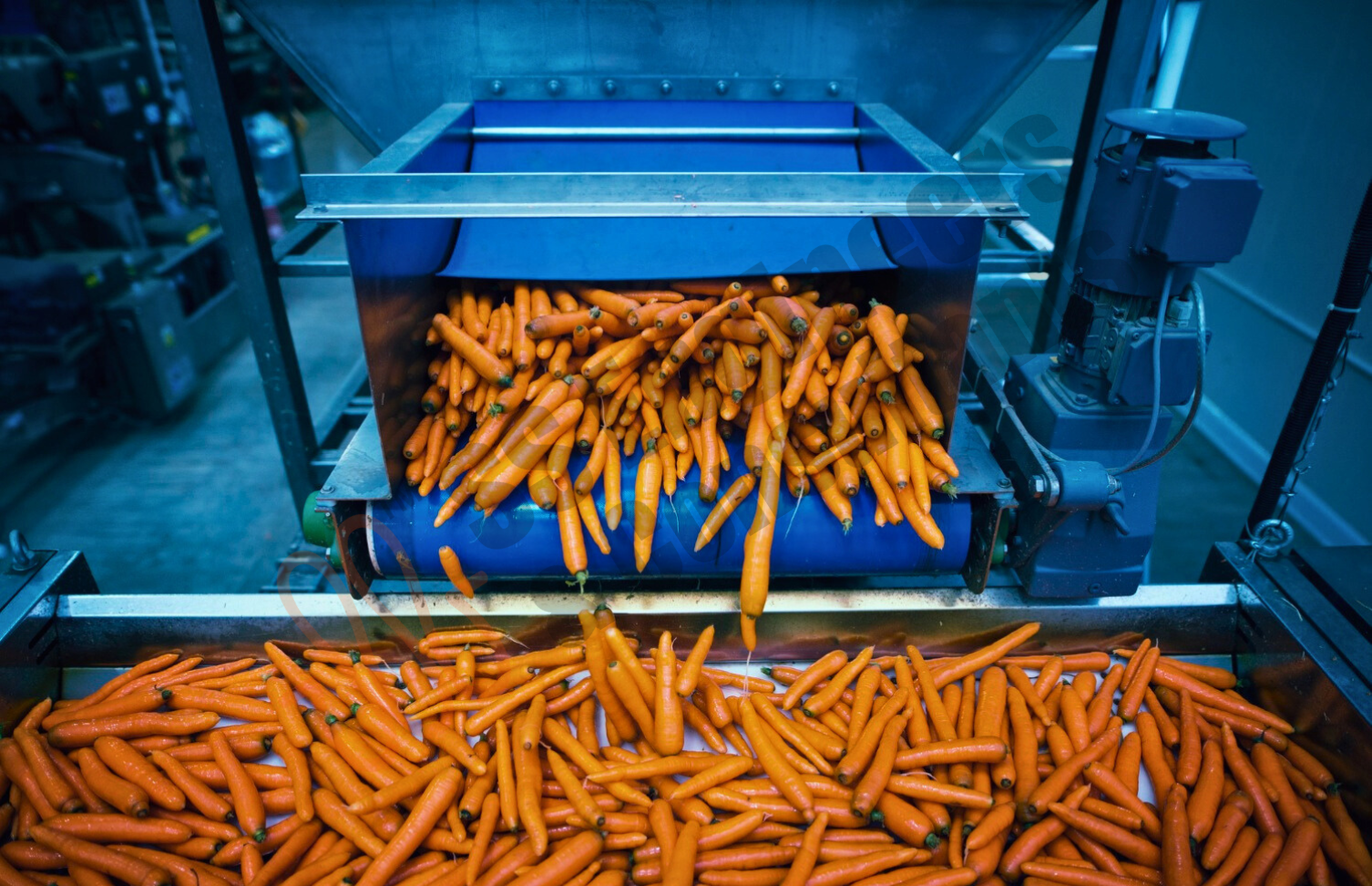

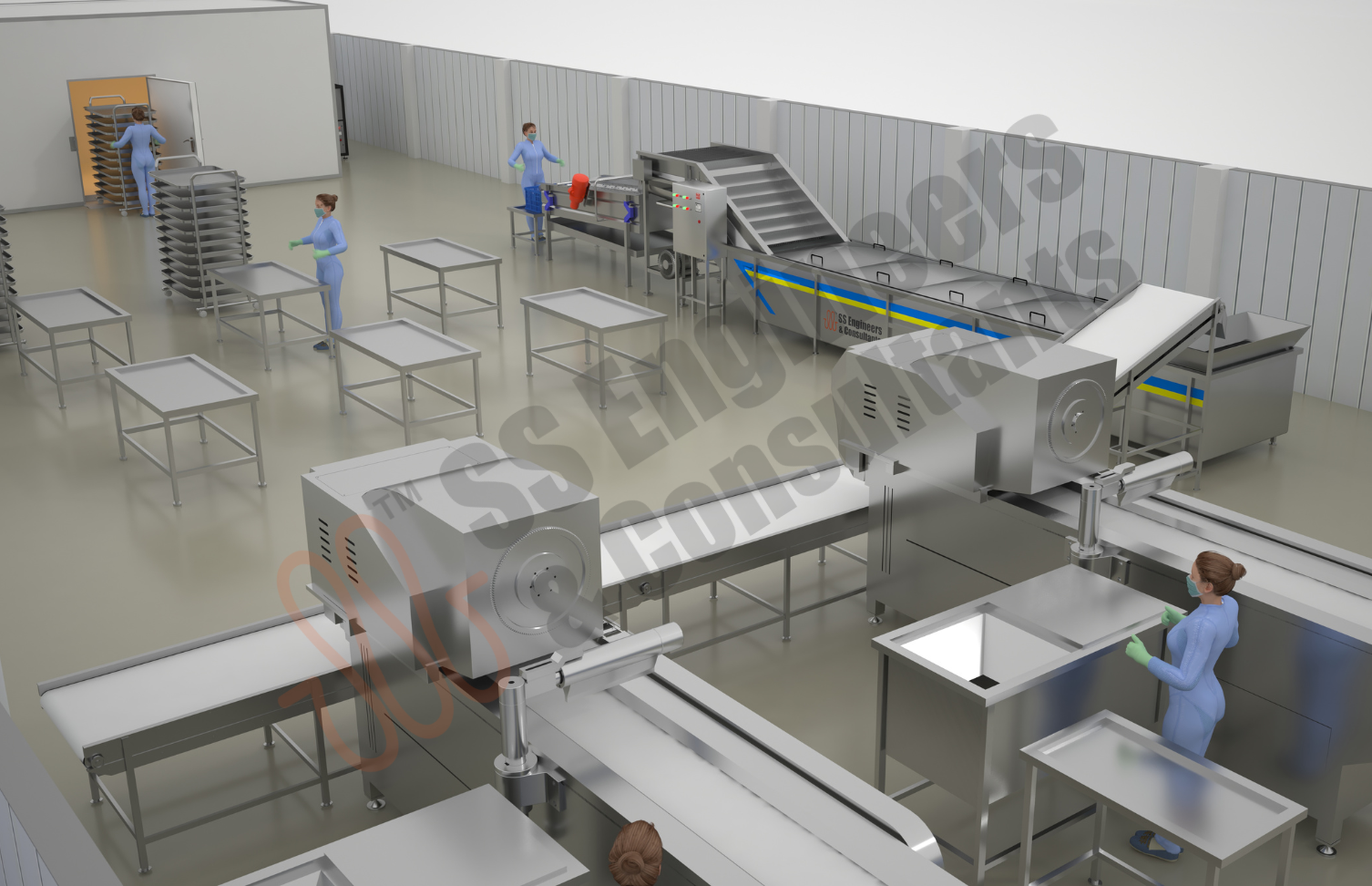
Extend the shelf life of perishable foods with SS Engineers & Consultants’ advanced Fruits & Vegetable Pack House solutions, designed to maintain freshness in bananas, fruits, vegetables, and more. Our technology minimizes spoilage and supports efficient, high-quality handling for the fresh produce industry.
Benefit from our dedication to innovation and research, which distinguishes us from competitors. By integrating premium components into every system, we deliver durability, reliability, and top-tier performance in all our fresh produce solutions.
- Robust stainless-steel construction ensuring hygiene and long-lasting durability
- Automated washing, sorting, and grading system for consistent quality of produce
- Integrated CIP (Clean-in-Place) system for quick and hygienic cleaning
- Precise temperature and humidity control to maintain freshness and extend shelf life
- Modular design adaptable for various fruits and vegetable types and capacities
- Compatible with fresh, leafy, root, and exotic produce for versatile handling
- Energy-efficient refrigeration and handling technology to minimize operating costs
See it in Action
Need Custom Solutions?
Our team can develop specialized cleaning solutions tailored to your specific automotive cleaning requirements.
Contact Our Experts